Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillation
Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillationOuchi, Kazuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Hirose, Kazuki*; Kurosawa, Yuika*; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shibukawa, Masami*; Saito, Shingo*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1298, p.342399_1 - 342399_7, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0Given that conventional methods of high-dose sample analysis pose substantial exposure risks and generate large amounts of secondary radioactive waste, faster procedures allowing for decreased radiation emission are highly desirable. To address this need, we developed a  Sr
Sr quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed
quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed  Sr
Sr in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify
in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify  Sr
Sr in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Osaka University*
JAEA-Review 2023-039, 71 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Improvement of aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometer for on-line measurement of tiny particles containing alpha emitters" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to improve Aerosol Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometer in order to monitor tiny particles containing alpha emitters such as U and Pu generated in removing debris from the reactors of 1F. In FY2021, for improving mass-resolution, we designed the optimized structure of mass spectrometer with much better mass resolution and ion transmittance than commercial ATOFMS by a PC simulation. Further, design of a detection part of ATOFMS fitted to the mass spectrometer was completed.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2023-025, 117 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of extremely small amount analysis technology for fuel debris analysis" conducted in FY2022. Understanding the properties of fuel debris is necessary for handling, criticality control, storage control, etc. A key technique is the chemical analysis of actinide nuclides. We develop sample pretreatment technology and separation / analysis process required for chemical analysis. The purpose of this study is to streamline future planned fuel debris analysis. To promote 1F decommissioning, we will train human resources through on-the-job training.
Kamada, Masaki*; Yoshida, Takuma*; Sugita, Tsukasa*; Okumura, Keisuke
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(2), p.83 - 86, 2024/02
, 66(2), p.83 - 86, 2024/02
no abstracts in English
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154799_1 - 154799_20, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal conductivities of near-stoichiometric (U,Pu,Am)O doped with Nd
doped with Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O , which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT)
, which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT) . The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C
. The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C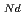 and C
and C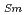 , respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70
, respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70  10
10 + 0.93C
+ 0.93C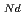 + 1.20C
+ 1.20C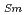 , B(m/W)=2.39
, B(m/W)=2.39  10
10 .
.
Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Matsumoto, Saori*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Hayashi, Kiichiro*; Endo, Rie*; Bell , M. R.*; Neubert, L.*; Volkova, O.*
, M. R.*; Neubert, L.*; Volkova, O.*
Steel Research International, p.2300766_1 - 2300766_6, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0The density of Ni-based superalloys is measured using the maximum bubble pressure (MBP) method. The viscosity is evaluated using the oscillating crucible method. The surface tension is simultaneously measured using the MBP method.
Fukahori, Tokio; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 65(12), p.726 - 727, 2023/12
, 65(12), p.726 - 727, 2023/12
The Investigative Committee on Nuclear Data investigates and observes global trends in nuclear research and development and conducts comprehensive examinations of Japanese nuclear data activities from a broader perspective, as well as cooperation with domestic and foreign academic institutions in a wide range of fields other than the Atomic Energy Society. We aim to establish a system for communication, information exchange, and interdisciplinary cooperation. In this report, we will report on three of the main activities for the 2021-2022 term: a request list site for nuclear data, human resource development, and roadmap production.
Tuya, D.; Nagaya, Yasunobu
Journal of Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 4(4), p.691 - 710, 2023/11
The Monte Carlo method is used to accurately estimate various quantities such as k-eigenvalue and integral neutron flux. However, when a distribution of a quantity is desired, the Monte Carlo method does not typically provide continuous distribution. Recently, the functional expansion tally and kernel density estimation methods have been developed to provide continuous distribution. In this paper, we propose a method to estimate a continuous distribution of a quantity using artificial neural network (ANN) model with Monte Carlo-based training data. As a proof of concept, a continuous distribution of iterated fission probability (IFP) is estimated by ANN models in two systems. The IFP distributions by the ANN models were compared with the Monte Carlo-based data and the adjoint angular neutron fluxes by the PARTISN code. The comparisons showed varying degrees of agreement or discrepancy; however, it was observed that the ANN models learned the general trend of the IFP distributions.
Shimada, Taro; Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Miwa, Kazuji; Takai, Shizuka; Takeda, Seiji
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/10
Nuclear regulatory inspection should be performed on the basis of the risk information during the decommissioning phase of the nuclear power plant. However, it is difficult because the methodology for quantitatively assessing the radiation exposure risk during decommissioning activities has not been established. Therefore, a decommissioning risk assessment code, DecAssess-R, has been developed based on the decommissioning safety assessment code, DecAssess, which creates event trees from initiating events and evaluates the radiation risk resulting from public exposure dose for each accident sequence. The assessment took into account that mobile radioactive inventories that can be easily dispersed in the work area, such as radioactive dust accumulated in HEPA filters attached to a contamination control enclosure, will fluctuate with the progress of the decommissioning work. Initiating events were selected based on the investigation of accidents and malfunctions during dismantling, disassembly, and component replacement activities around the world, and event trees were created from the initiating events to indicate the progress scenario. The frequencies of occurrence were determined with reference to general industry data in addition to the above accidents and malfunctions, and the probabilities of event progression were determined with reference to failure data during the operation phase. The exposure risks during dismantling of components in the reference BWR were evaluated. As a result, the public exposure dose was maximum in case of fire during dismantling of reactor internals and fire spread to combustibles and filters, including radioactivity temporarily stored in the work area. The exposure risk was also maximum because the probability of occurrence of this accident sequence was greater than that of other scenarios.
 B-enriched MgB
B-enriched MgB wire using a pulsed neutron source
wire using a pulsed neutron sourceMachiya, Shutaro*; Osamura, Kozo*; Hishinuma, Yoshimitsu*; Taniguchi, Hiroyasu*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.34_1 - 34_17, 2023/10
Suzuki, Seiya; Nemoto, Yoshihiro*; Shiiki, Natsumi*; Nakayama, Yoshiko*; Takeguchi, Masaki*
Annalen der Physik, 535(9), p.2300122_1 - 2300122_12, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Pla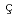 ais, A.*; Bouly, F.*; Yee-Rendon, B.
ais, A.*; Bouly, F.*; Yee-Rendon, B.
Proceedings of 14th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC 23) (Internet), p.4097 - 4100, 2023/09
Reliability in high power hadron accelerators is a major issue, particularly for Accelerator Driven Systems (ADS). For example, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) ADS maximum frequency of beam trips longer than 5 min was set to 42 per year. A significant number of breakdowns are caused by the failure of accelerating cavities or by their associated systems. Hence, we studied how these can be effectively reduced. To this end, we developed the numerical tool LightWin that aims to determine the compensation settings for any superconducting (SC) linac automatically and systematically. This tool has been successfully used for the MYRRHA SC linac. In this work, we applied LightWin to compensate for several failure scenarios involving the last section of the JAEA ADS linac and compared the associated retuned settings and beam performance to those found in a previous study with TraceWin.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2023-001, 38 Pages, 2023/07
Research on advanced computational science for nuclear applications, based on "the plan to achieve the medium- and long-term goal of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency", has been performed by Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE), Japan Atomic Energy Agency. CCSE established a committee consisting of external experts and authorities which evaluates and advises toward the future research and development. This report summarizes the results of the R&D performed by CCSE in FY2022 (April 1st, 2022 - March 31st, 2023) and their evaluation by the committee.
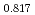 Pu
Pu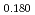 Am
Am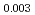 O
O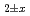 uranium-plutonium-americium mixed oxides at 1573, 1773, and 1873 K
uranium-plutonium-americium mixed oxides at 1573, 1773, and 1873 KVauchy, R.; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Hirooka, Shun; Nakamichi, Shinya; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 580, p.154416_1 - 154416_11, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:98.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tokunaga, Sho; Horiguchi, Hironori; Nakamura, Takemi
JAEA-Technology 2023-001, 37 Pages, 2023/05
The cold neutron source (CNS) of the research reactor JRR-3 converts thermal neutrons generated in the reactor into low-energy cold neutrons by moderating them with liquid hydrogen stored in the moderator cell. Cold neutrons generated by the CNS are transported to experimental instruments using neutron conduits, and are used for many studies of physical properties, mainly in life science, polymer science, environmental science, etc. Improvement of cold neutron intensity is essential to maintain competitiveness with the world's research reactors in neutron science, and we are developing a new CNS that incorporates new knowledge. The current moderator cell for the CNS of JRR-3 is a stainless-steel container which is a canteen bottle type, and the cold neutron intensity can be improved by changing the material and shape. Therefore, the basic specifications of the new moderator cell were changed to aluminum alloy which has a smaller neutron absorption cross section, and the shape was optimized using a Monte Carlo code MCNP. Since these changes in specifications will result in changes in heat generation and heat transfer conditions, the CNS of JRR-3 was re-evaluated in terms of self-regulating characteristic, heat transport limits, heat resistance and pressure resistance, etc., to confirm its feasibility in thermal-hydraulic design. This report summarizes the results of the thermal-hydraulic design evaluation of the new moderator cell.
Shiwaku, Hideaki; Marushita, Motoharu*
JAEA-Research 2022-015, 39 Pages, 2023/05
We designed the hard X-ray undulator beamline BL22XU, which is dedicated to Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) at SPring-8 (now Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA)). BL22XU is used for XAFS (X-ray Absorption Fine Structure) analysis experiments to develop separation and extraction materials for radioactive waste treatment and to elucidate their chemical behavior, magnetic research experiments using a diffractometer, and experiments under extreme conditions using a high-pressure press and a diamond anvil cell. The available X-ray energy range was set from 3 to 70 keV. To design the optics of the beamline, the reflectivity of the mirrors, the diffraction width of the monochromatic crystal, and the absorptance of the Be window were calculated. In addition, ray tracing was performed to optimize the materials for optics, dimensions, and location. The delay time of the ADL (Acoustic Delay Line) was also examined to ensure the safety in the use of radioactive materials. The operation of BL22XU "JAEA Actinide Science I" has already started. By collaborating BL22XU and BL23SU "JAEA Actinide Science II," which uses a soft X-ray undulator as a light source, we solve the problems to promote nuclear sciences. Since the monochromator was upgraded in 2018-2019, initial planning and measured data are documented here again.
Kurisaka, Kenichi
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
This study aims to understand a time trend of the occurrence rate of steam generator (SG) tube leak in the existing sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs) based on the observed data. The target on SFRs in the present paper is Phenix in France and BN600 in Russia. From the open literature review, we investigated the number of tube-to-tube plate weld, the number of tube-to-tube weld, heat transfer area of tube base metal, operating time of SGs, dates when SG tube leak occurred, leaked location, corrective action after tube leak such as replacement of leaked module. Based on these observed data, time to leak is estimated and then time trend of the occurrence rate of SG tube leak for each of the above-mentioned parts was quantitatively analyzed by the hazard plotting method. As a result, the rate of leak at tube-to-tube weld in Phenix shows increase with time due to probable cause of cyclic thermal stress in a short term. As for a long-term trend, the rate of tube leak in both Phenix and BN600 SGs indicated decrease with time probably thanks to improvement in welding and in SG operating condition and to removal of initial failure.
Li, C.-Y.; Watanabe, Akira*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Yamazaki, Yasuhiro*; Shinomiya, Keisuke*; Okumura, Tadaharu*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Nakamura, Yuiga*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.14_1 - 14_12, 2023/05
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-072, 116 Pages, 2023/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge of novel hybrid-waste-solidification of mobile nuclei generated in Fukushima Nuclear Power Station and establishment of rational disposal concept and its safety assessment" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to establish the rational waste disposal concept of a variety of wastes generated in 1F by the novel hybrid-waste-solidification. The phosphate form of ALPS sediment wastes containing Eu , Ce
, Ce , Sr
, Sr and Cs
and Cs were synthesized as well as radioactive
were synthesized as well as radioactive  Sr,
Sr,  Cs and
Cs and  I which are both
I which are both  emitters, AREVA sludge and Iodine Calcium apatite were synthesized, and they were processed to the stabilization treatment such as sintering and Spark Plasma ...
emitters, AREVA sludge and Iodine Calcium apatite were synthesized, and they were processed to the stabilization treatment such as sintering and Spark Plasma ...